
Proper training and exercise can help reduce the risk of ACL injury. Multiple factors likely influence the risk of arthritis, such as the severity of the original injury, the presence of related injuries in the knee joint or the level of activity after treatment. Arthritis may occur even if you have surgery to reconstruct the ligament. People who experience an ACL injury have a higher risk of developing osteoarthritis in the knee. Using poorly maintained sports equipment, such as ski bindings that aren't adjusted properly.Wearing footwear that doesn't fit properly.Using faulty movement patterns, such as moving the knees inward during a squat.Participating in certain sports, such as soccer, football, basketball, gymnastics and downhill skiing.Being female - possibly due to differences in anatomy, muscle strength and hormonal influences.There are a number of factors that increase your risk of an ACL injury, including: A mild injury may stretch the ligament but leave it intact. When the ligament is damaged, there is usually a partial or complete tear of the tissue.

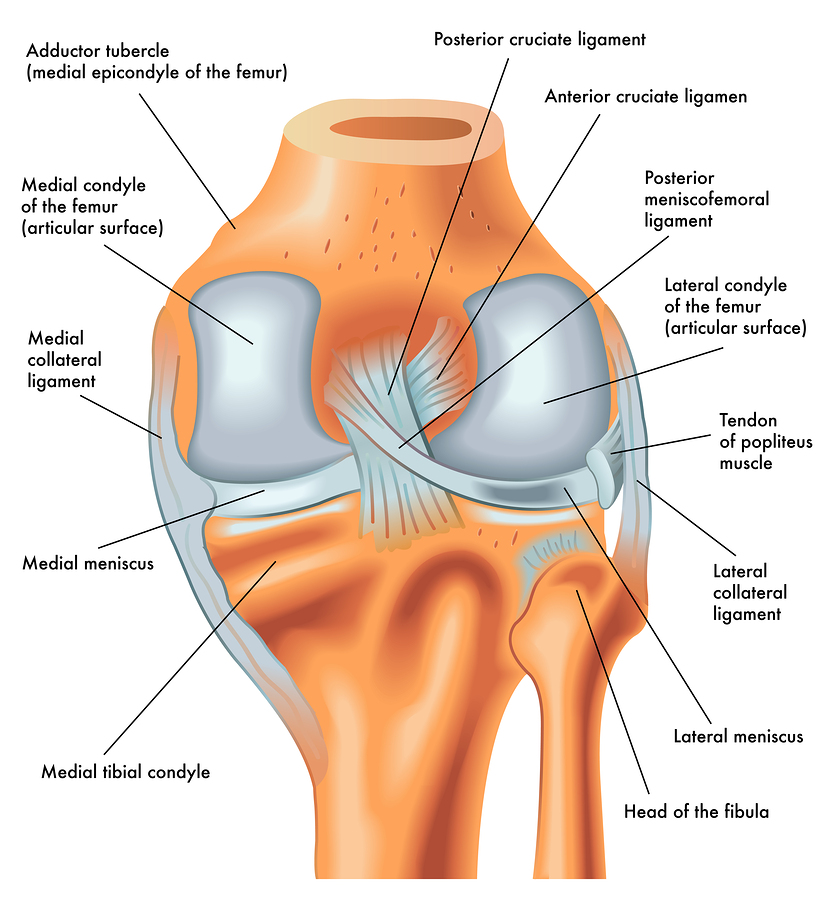
Receiving a direct blow to the knee or having a collision, such as a football tackle.Suddenly slowing down and changing direction (cutting).The ACL, one of two ligaments that cross in the middle of the knee, connects your thighbone to your shinbone and helps stabilize your knee joint.ĪCL injuries often happen during sports and fitness activities that can put stress on the knee: Ligaments are strong bands of tissue that connect one bone to another. Request an Appointment at Mayo Clinic Causes


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
